Submit your review | |
Support and resistance are fundamental concepts in technical analysis, serving as key indicators for traders to identify potential price reversals and breakouts. Understanding how to effectively use support and resistance levels can enhance trading strategies, improve risk management, and guide entry and exit points.
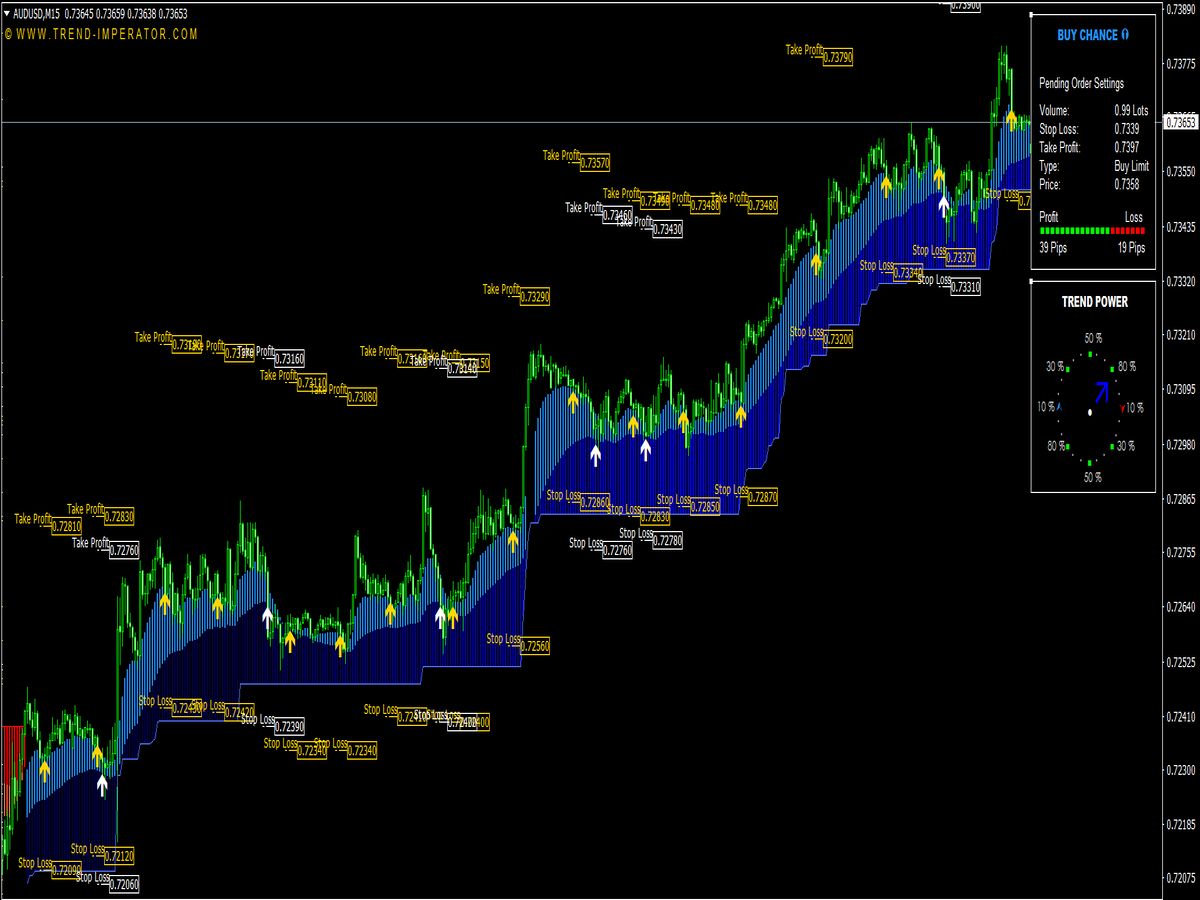
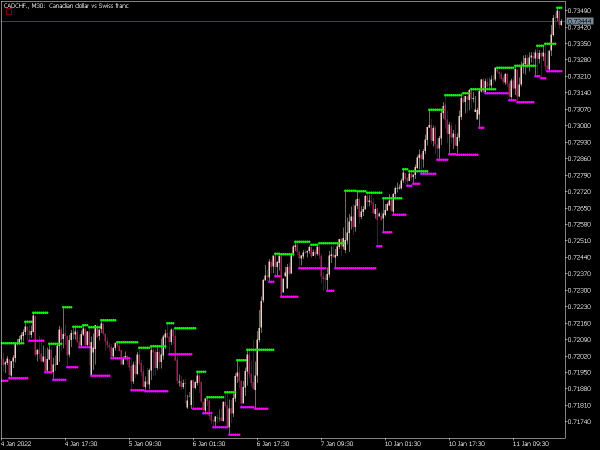
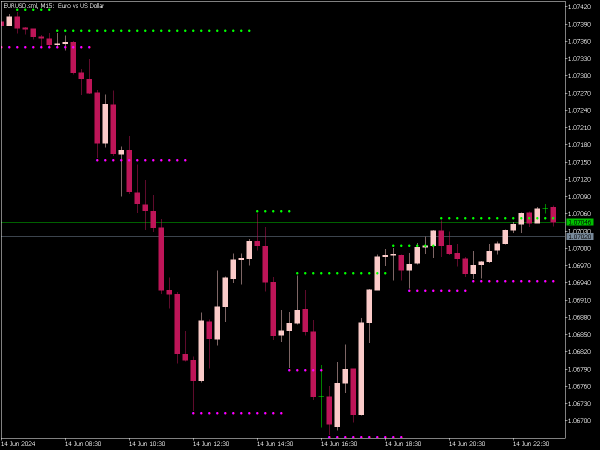
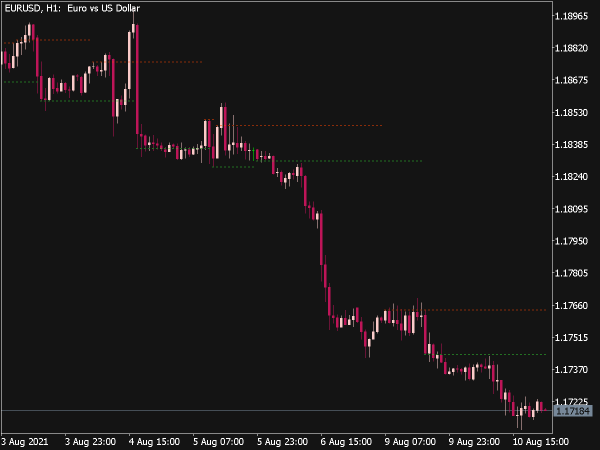
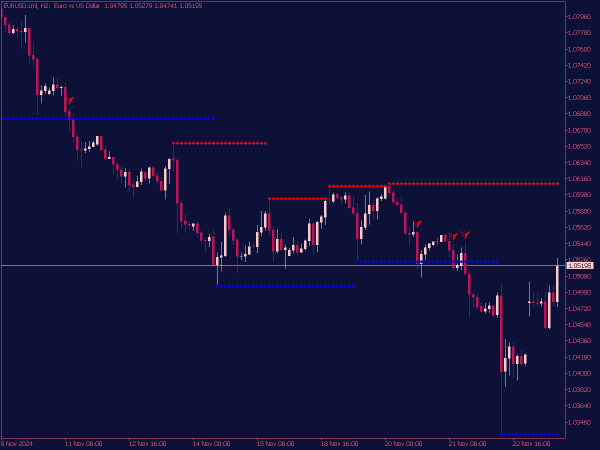
Support Level: This is a price point where buying interest is strong enough to overcome selling pressure. Typically, when the price approaches a support level, it is expected to bounce back, making it an ideal area for traders to consider entering long positions.
Resistance Level: Conversely, a resistance level is where selling pressure overwhelms buying interest, causing the price to reverse downward. When prices hit a resistance level, it often indicates a good opportunity to enter short positions.
Traders systematically analyze historical price data to identify these levels, using them as benchmarks for future price movement. A strong support level will be tested multiple times without being broken, while a significant resistance level will similarly resist upward movement.
How to Identify Support and Resistance Levels
1. Historical Price Action: Review historical price charts to pinpoint areas where the price has reversed multiple times. These are strong candidates for support and resistance.
2. Trendlines: Draw trendlines that connect highs and lows on a price chart. Trendlines can indicate dynamic support and resistance levels that adjust with the market.
3. Moving Averages: Often used as dynamic support and resistance levels, moving averages, such as the 50-day or 200-day, can help traders gauge potential price reversals and support areas.
4. Fibonacci Retracement: This tool allows traders to predict potential reversal levels based on the Fibonacci sequence. Key levels include 23.6%, 38.2%, 50%, 61.8%, and 78.6%, which often act as support or resistance.
5. Psychological Levels: Round numbers, such as 50, 100, or 1000, can act as psychological support and resistance levels since traders often set orders around these numbers.
Trading Strategies with Support and Resistance
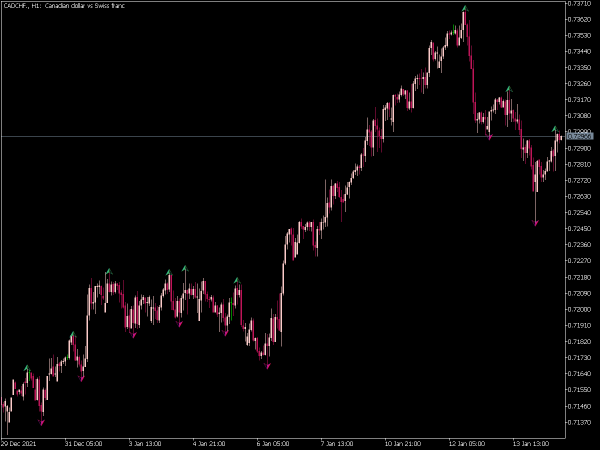
1. Bounce Trading: This strategy involves entering a trade when the price bounces off a support or resistance level. For example, a trader might place a buy order when the price approaches a strong support level, anticipating a bounce. Confirmation via candlestick patterns or volume can help validate the bounce.
2. Breakout Trading: A breakout occurs when the price moves outside established support or resistance levels. To trade this strategy, wait for confirmation, such as a close beyond the level, and enter the market. A high trading volume can signal the strength of the breakout, supporting the validity of the move.
3. Retest Strategy: After a breakout, many traders wait for the price to retest the broken level. If a resistance level is breached and then retested before continuing higher, that level can convert to support. Entering the market on this retest can provide a favorable risk-to-reward ratio.
4. Range Trading: In a ranging market, traders can capitalize on the price oscillating between established support and resistance levels. Purchasing at support and selling at resistance allows for relatively low-risk trades.
5. Trend Continuation: Recognize whether the market is trending (either upward or downward) and use the trend to your advantage. In a bullish trend, look for support levels to enter long positions, and in a bearish trend, focus on resistance levels for shorting opportunities.
Incorporating Indicators with Support and Resistance
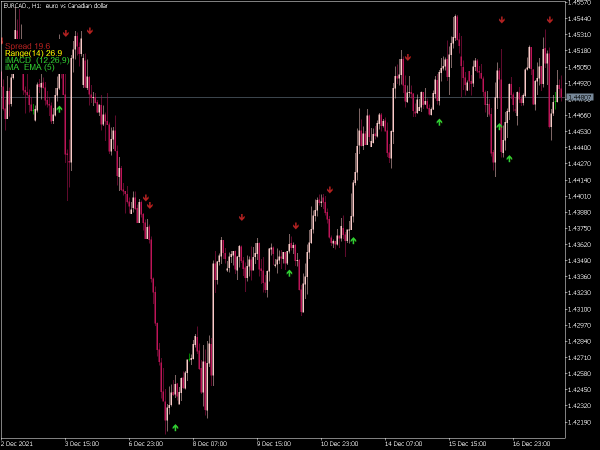
1. Relative Strength Index (RSI): This momentum oscillator can be used alongside support and resistance to identify overbought or oversold conditions, enhancing entry and exit decisions. If the price approaches support while the RSI shows oversold conditions, this can indicate a potential buying opportunity.
2. Moving Averages Crossovers: Combining support and resistance with moving averages can provide additional context. A moving average crossing above a resistance level (especially a slow-moving average) can signal a potential bullish breakout.
3. Volume Indicators: High trading volume at support or resistance levels can indicate strong interest, lending confidence to a trader’s decisions regarding these levels. For instance, an increase in volume during a breakout can validate the strength of the new trend.
4. Bollinger Bands: These bands can serve as dynamic support and resistance levels while providing insights into volatility. Traders often look for price to bounce off the bands or to break through them to make trading decisions.
Risk Management
Implementing effective risk management strategies is essential when trading based on support and resistance.
• Stop-Loss Orders: Always place stop-loss orders below support levels when buying and above resistance levels when selling. This practice helps minimize losses in case the price moves unfavorably.
• Position Sizing: Adjust your position size based on the distance to the nearest support or resistance level. The tighter the stop-loss, the larger the position you can afford while still managing risk.
• Profit Targets: Determine profit targets based on the next key support or resistance level. This can provide a clear exit strategy and help traders maintain discipline.
Conclusion
Utilizing support and resistance levels effectively can enhance a trader's decision-making process, improving the chances of successful trades. Developing a solid understanding of how to identify these levels, applying various trading strategies, and incorporating additional indicators will lead to more informed trading decisions.
Remember to continuously assess market conditions, remain adaptable, and exercise prudent risk management to navigate the complexities of trading successfully. This holistic approach to trading with support and resistance will foster long-term profitability and resilience in dynamic market environments.