Submit your review | |
Scalping is a trading strategy aimed at generating small profits from tiny price changes in highly liquid markets. Traders who employ this method, known as scalpers, frequently make multiple trades within short periods, sometimes within seconds or minutes. The effectiveness of scalping often hinges on leveraging specific technical indicators to make informed trading decisions.
Before diving into trading strategies, it's essential to understand the fundamentals of scalping. Scalpers typically focus on highly liquid markets, such as forex, futures, or major stock indices, where price movements are more frequent and significant opportunities are created. These traders often rely on technical indicators to analyze price action, identify trends, and find optimal entry and exit points.
Key Indicators for Scalping
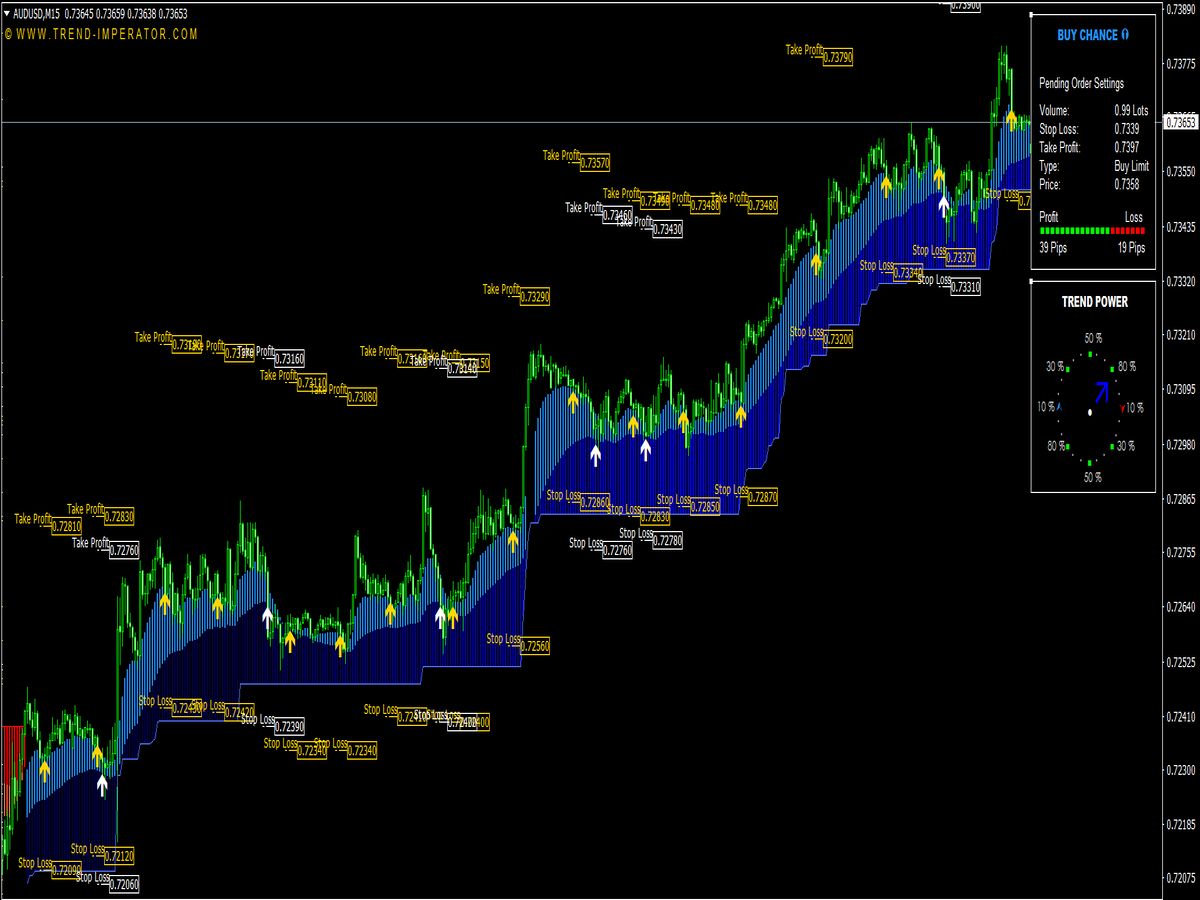
1. Moving Averages (MA): Moving averages smooth out price data to create a trend-following indicator. In scalping, traders often use short-term moving averages, such as the 5-period or 10-period moving averages, to track immediate price action. A common strategy is to generate a buy signal when the short-term MA crosses above a longer-term MA, and a sell signal when it crosses below.
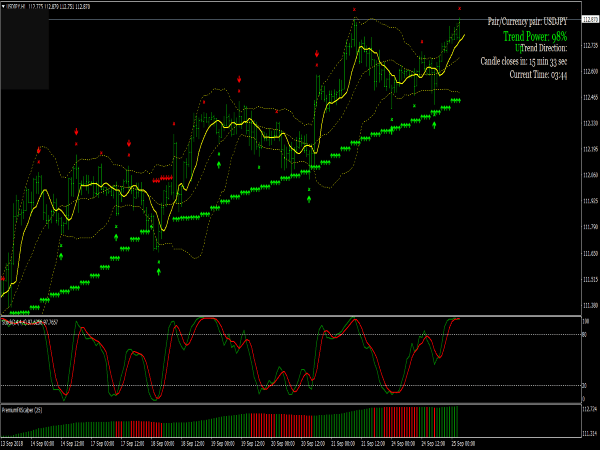
2. Relative Strength Index (RSI): The RSI measures the speed and change of price movements, ranging from 0 to 100. Scalpers often look for RSI levels above 70 (indicating overbought conditions) or below 30 (indicating oversold conditions) to make quick trades. A common approach is to enter a long position when the RSI crosses back above 30 and a short position when it falls below 70.
3. Stochastic Oscillator: This momentum indicator compares a particular closing price of a security to a range of its prices over a certain period. In scalping, traders often look for crossovers, particularly when the stochastic lines (the %K and %D lines) cross in overbought or oversold territory. For instance, a buy signal is generated when the %K line crosses above the %D line below 20.
4. Bollinger Bands: These consist of a middle band (the simple moving average) and two outer bands. The outer bands indicate volatility and potential price reversals. A strategy involves buying when the price touches the lower band and selling when it reaches the upper band. This approach is particularly effective in ranging markets.
5. Volume Indicators: Volume plays a crucial role in confirming price movements. Indicators like On-Balance Volume (OBV) or the Volume Weighted Average Price (VWAP) help traders gauge the strength of price moves. For scalping, look for increased volume to confirm breakouts or reversals.
Moving Average Crossover Strategy
One popular scalping strategy is the moving average crossover. Traders utilize two moving averages: a short-term and a long-term MA.
• Entry Point: Enter a long position when the short-term MA (like the 5-period) crosses above the long-term MA (like the 20-period). Conversely, enter a short position when the short-term MA crosses below the long-term MA.
• Exit Point: Set a tight stop-loss just below the last swing low for long trades and above the last swing high for short trades. Consider exiting once you achieve a 1:1 risk-to-reward ratio.
Scalping Strategy with RSI & Bollinger Bands
Combining the RSI and Bollinger Bands can provide effective scalping signals in volatile markets.
• Entry Point: Buy when the price touches the lower Bollinger Band and the RSI is below 30. Sell when the price touches the upper Bollinger Band and the RSI is above 70.
• Exit Point: Set a tight stop-loss just outside the opposite Bollinger Band and look to take profits as the price moves back toward the middle band.
Trading Strategy with Stochastic Oscillator & Support/Resistance
Using the stochastic oscillator alongside support and resistance levels can enhance the probability of successful trades.
• Entry Point: Identify key support and resistance levels. Buy when the stochastic oscillator indicates oversold conditions (crossing back above 20) near support. Conversely, sell when it indicates overbought conditions (crossing back below 80) near resistance.
• Exit Point: Place stop-loss orders beyond the support or resistance levels and aim for a target based on a fixed risk-to-reward ratio.
Risk Management and Best Practices
Success in scalping is not just about finding the right indicators, effective risk management is crucial. Here are key considerations:
• Use Tight Stop-Loss Orders: Given the fast nature of scalping, setting tight stop-loss orders helps protect against significant losses.
• Limit the Number of Trades: Rather than overtrading, choose high-probability setups based on your indicators.
• Stay Aware of Market Conditions: Market volatility can greatly impact scalping strategies. Avoid trading during high-impact news events unless you are skilled in managing such volatility.
• Practice with a Demo Account: Before moving into the live market, practice your strategies with a demo account to refine your skills without risking real capital.
Conclusion
Scalping can be a rewarding trading strategy when implemented with the right tools and methodologies. By utilizing indicators such as moving averages, RSI, stochastic oscillators, Bollinger Bands, and volume indicators, traders can enhance their decision-making process for quick trades.
However, traders must remember that risk management and emotional discipline play substantial roles in achieving long-term success in scalping. With practice, patience, and continuous learning, it’s possible to develop a strong scalping strategy that yields positive results in volatile markets.
Very accurate
Very good indicator.
super fast indicator