Submit your review | |
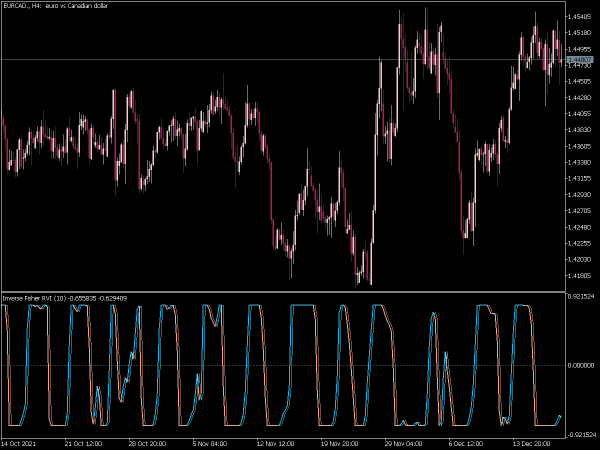
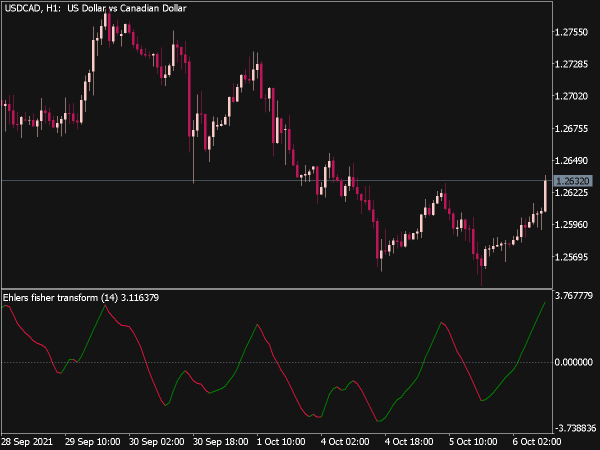
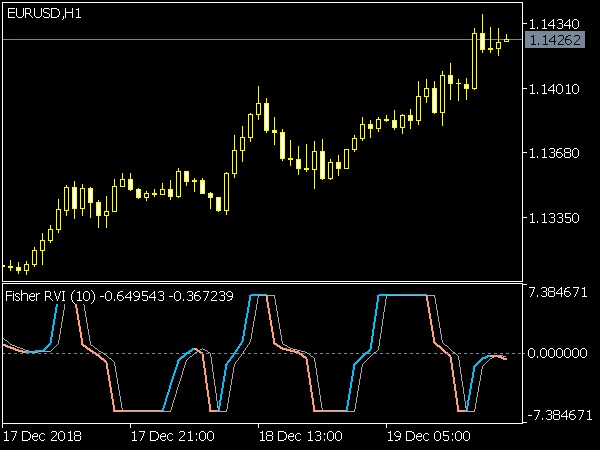
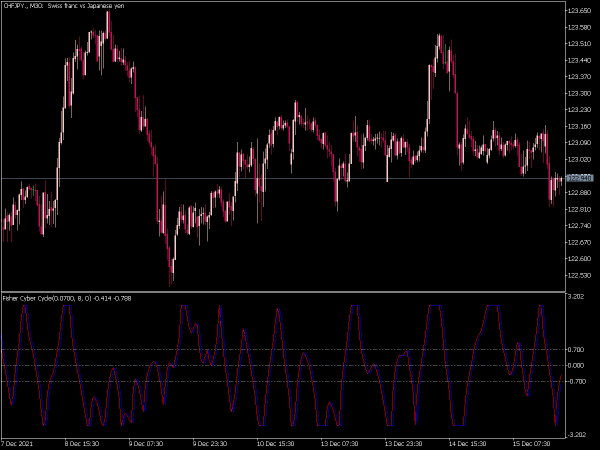
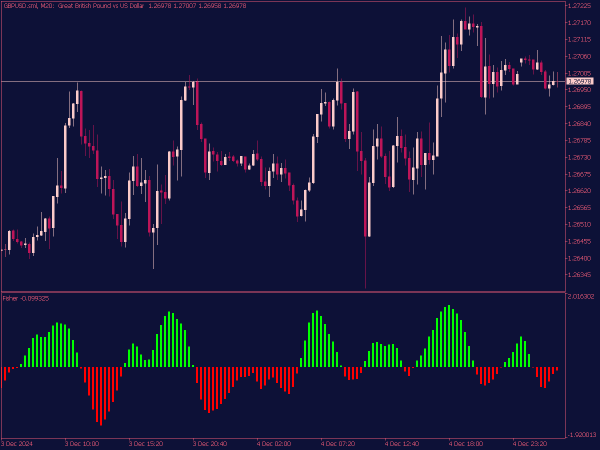
The Fisher Indicator is a technical analysis tool used to identify potential reversal points in the price of an asset. It is based on the concept of the Fisher Transform, which applies a mathematical transformation to price data to produce a series of values that resemble a normal distribution. This helps traders detect overbought or oversold conditions more effectively.
Typically, values above 1.5 or below -1.5 may signal strong momentum, while values around zero indicate potential consolidation or reversal zones. The Fisher Indicator is often used in conjunction with other indicators to enhance trading strategies.
Here are some trading strategies based on the Fisher Indicator:
1. Basic Buy/Sell Signals: Enter a buy position when the Fisher Indicator crosses above a predetermined threshold (e.g., 0.5) and sell when it crosses below a lower threshold (-0.5). This approach capitalizes on momentum shifts.
2. Divergence Trading: Look for divergences between the Fisher Indicator and price action. If the price makes a new high but the Fisher Indicator does not, it indicates potential weakness, prompting a sell signal. Conversely, if the price hits a new low but the Fisher shows strength, consider a buy opportunity.
3. Trend Following: Use the Fisher Indicator in conjunction with other trend indicators (like moving averages). Enter long positions when the Fisher crosses above 0, confirming an upward trend, and short positions when it crosses below -0.5, suggesting a downtrend.
4. Pullback Strategy: After a strong price move, wait for the Fisher Indicator to pull back into the neutral zone (-0.5 to 0.5). Enter trades in the direction of the prevailing trend when the indicator returns to the threshold levels.
5. Combination with Other Indicators: Enhance the effectiveness of the Fisher Indicator by combining it with other tools like RSI or MACD. For example, if the Fisher Indicator generates a buy signal while RSI is below 30 (oversold), the likelihood of a rebound increases.
6. Stop Loss and Take Profit: Integrate risk management by setting stop losses below recent swing lows for buy trades and above recent highs for sell trades. Set take-profit targets using Fibonacci retracement levels or previous support/resistance levels.
7. Timeframe Considerations: Tailor trading strategies to different timeframes. While short-term traders might focus on 5-minute or 15-minute charts, longer-term traders may utilize daily or weekly charts for broader market trends.
8. Market Conditions: Be mindful of market conditions when applying Fisher Indicator strategies. In highly volatile markets, signals can be prone to false positives. Employ additional filtering methods to confirm signals.
These strategies require backtesting and practice to adapt to changing market conditions for the best results. Always ensure proper risk management to safeguard against adverse market movements.