Submit your review | |
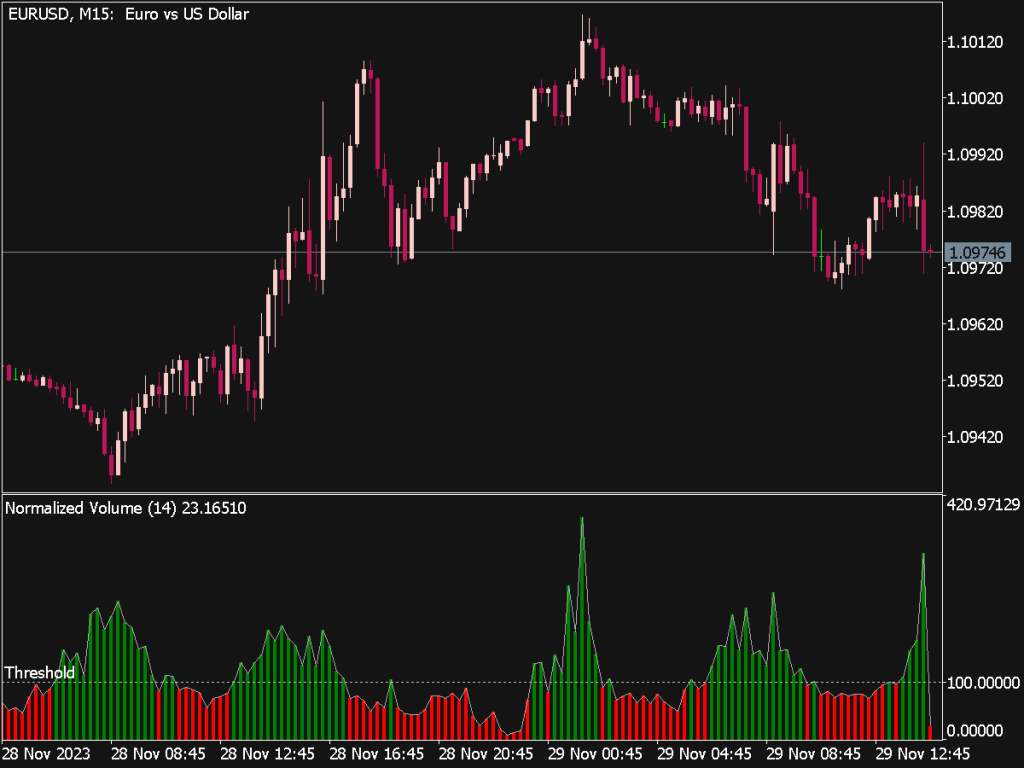
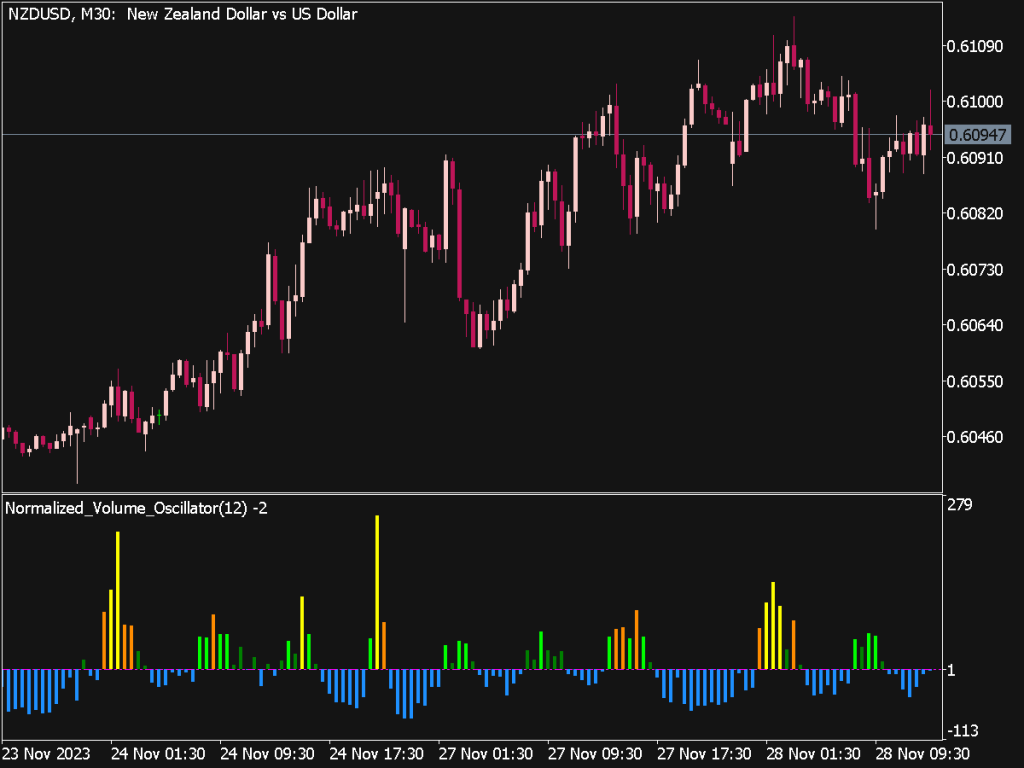
The Normalized Volume Oscillator (NVO) is a versatile trading tool that helps traders track volume changes relative to a moving average, providing insights into potential price movements. To effectively integrate the NVO into your trading strategy, consider the following tips and strategies.
1. Understanding the NVO: The NVO calculates the difference between two moving averages of volume (typically, a shorter and a longer period). A positive NVO indicates rising volume relative to its average, while a negative NVO signifies declining volume. Traders often use this indicator to confirm price trends or potential reversals.
2. Identifying Trends: When the NVO is above zero, it suggests that buying interest is strong, which may signal a continuation of the bullish trend. Conversely, an NVO below zero may indicate bearish sentiment. Traders can use these signals in conjunction with price action to identify strong trends and place trades that align with the prevailing market momentum.
3. Divergence Signals: Look for divergence between the NVO and price action, as this may signal potential reversals. For instance, if prices reach new highs while the NVO shows lower highs, this divergence may indicate weakening momentum and a possible trend reversal. Such signals can be an excellent opportunity to enter short positions or tighten risk on long positions.
4. Volume Confirmation: Use the NVO in conjunction with other technical indicators such as Moving Averages, Relative Strength Index (RSI), or MACD. For example, if the NVO indicates increasing volume alongside a price breakout confirmed by a Moving Average crossover, this could serve as a strong buy signal.
5. Setting Entry and Exit Points: Incorporate the NVO into your entry and exit strategies. Enter long positions when the NVO turns positive, indicating increasing buying pressure, and consider exiting or reversing trades when it falls back to negative territory. Apply stop-loss orders just below significant support levels, adjusting them as the price and NVO evolve.
6. Timeframe Consideration: Depending on your trading style, use different timeframes. Day traders may prefer shorter-term moving averages (e.g., 5-day and 20-day), while swing traders might opt for longer moving averages (e.g., 10-day and 50-day) to align with more extended market fluctuations. The method to select moving averages will depend on your risk tolerance and trading objectives.
7. Volume Thresholds: Establish volume thresholds that correspond with the NVO readings. A sudden increase in volume, when the NVO is positive, can be a strong indication of a breakout or continuation. Conversely, a spike in volume while the NVO is negative may indicate that selling pressure is intensifying, warranting caution.
8. Market Conditions: Be aware of overall market conditions. In trending markets, the NVO can provide reliable signals; however, in choppy or sideways markets, the signals may be less reliable. When implementing the NVO, consider additional factors such as broader economic indicators or market news that could influence volume and price dynamics.
9. Backtesting Strategies: As with any trading strategy, backtesting is essential. Analyze historical price and volume data to evaluate the effectiveness of your NVO strategy. Look for consistent patterns that yield positive results and adjust your approach based on empirical evidence before applying it to live trading.
10. Risk Management: Finally, integrate robust risk management practices when utilizing the NVO. Determine your risk-reward ratio, set stop-loss orders, and never risk more than a small percentage of your trading capital on a single trade. Risk management is crucial to longevity in trading, particularly as market conditions can change rapidly.
By applying these strategies with the Normalized Volume Oscillator, traders can enhance their approach to market analysis. The NVO serves as a valuable tool for understanding market sentiment and volume changes, aiding in making informed trading decisions while efficiently managing risk.