Submit your review | |
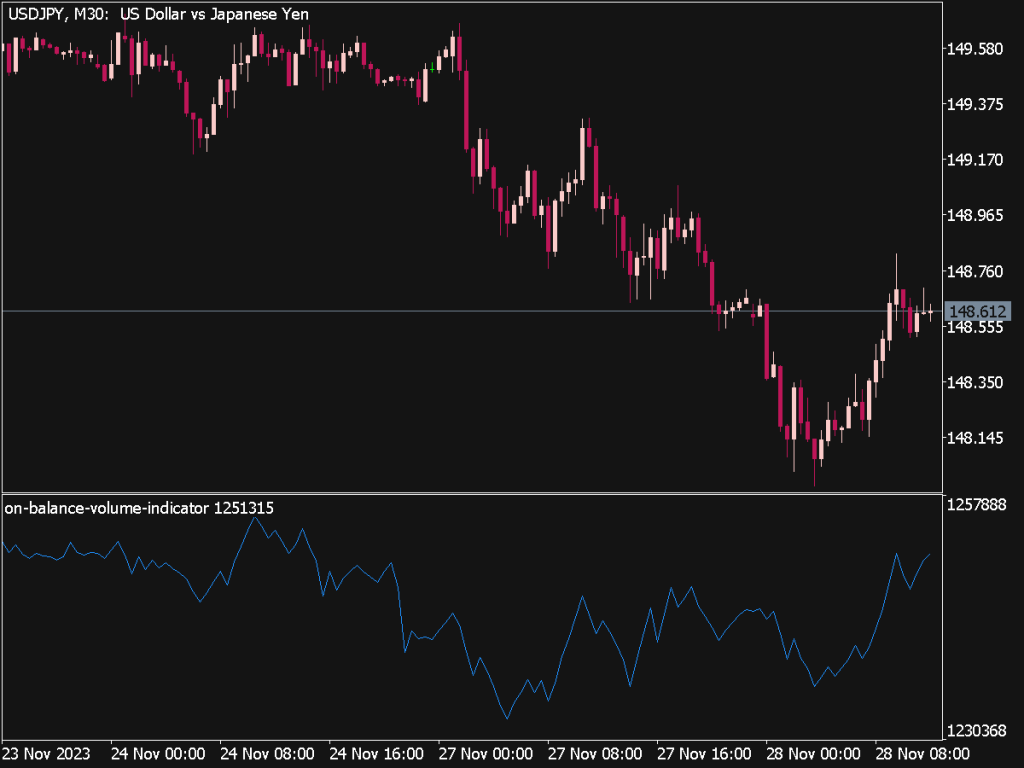
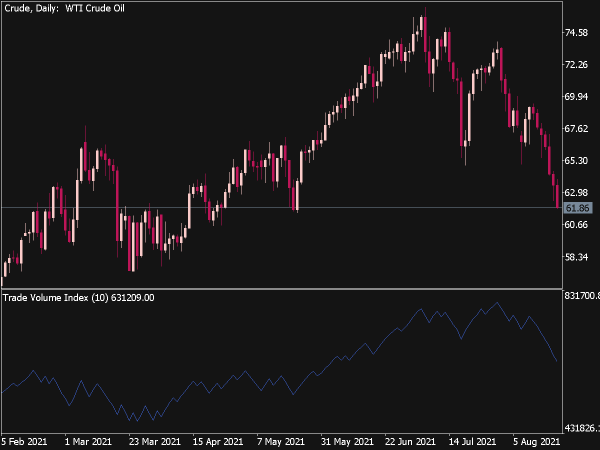
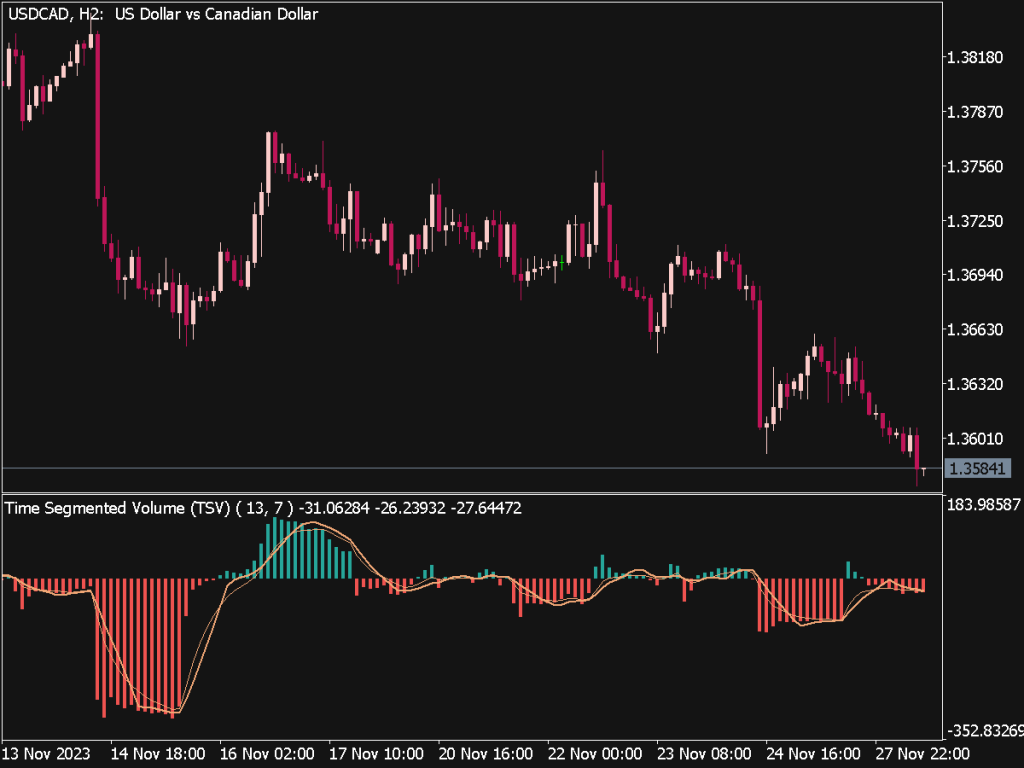
The Time Segmented Volume (TSV) Indicator is a versatile tool used in technical analysis to assess the strength or weakness of price movements based on volume data over specified time frames. Here are key trading tips and rules for effectively utilizing the TSV in your trading strategy:
1. Understanding TSV: The TSV measures the buying and selling pressure by calculating the volume associated with price movement direction. A rising TSV indicates increased buying interest, while a declining TSV suggests selling pressure.
2. Identifying Trends: Use the TSV to confirm trends. When the price is rising, observe whether the TSV rises concurrently. If both the price and TSV increase, it signals strong bullish sentiment. Conversely, if the price rises while the TSV declines, it indicates potential weakness — a divergence that could signal a reversal.
3. Divergence Signals: Watch for divergence between the TSV and price action. For example, if the price reaches a new high but the TSV does not (or vice versa), it may indicate a weakening trend and potential reversal. This is a critical cue for traders to reconsider their positions.
4. Combining Indicators: Enhance the effectiveness of the TSV by combining it with other indicators, such as moving averages, RSI, or MACD. For instance, if both the TSV and RSI are predicting a shift in momentum, this confluence increases the reliability of your trading decision.
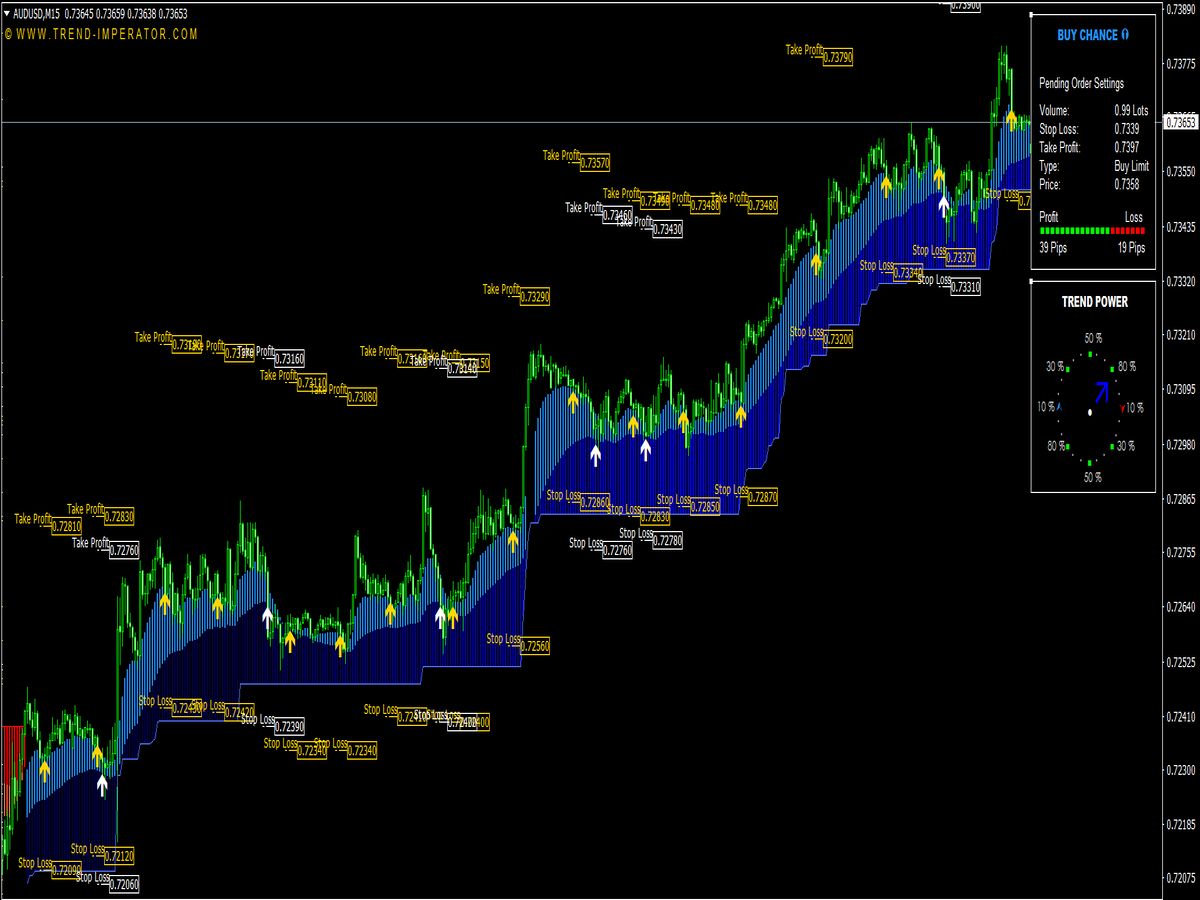
5. Entry and Exit Points: Utilize the TSV indicator to fine-tune your entry and exit points. Enter long positions when the TSV crosses above zero and shows upward momentum, and consider exiting or selling when it begins to decline or when it illustrates divergence from price movement.
6. Time Frame Consideration: The effectiveness of the TSV can vary significantly across different time frames. Day traders might use shorter time frames (like 5 or 15 minutes) to identify quick opportunities, while swing traders may focus on hourly or daily charts for more substantial trends. Adjusting the time frame allows you to tailor the indicator to your trading style.
7. Volume Profiles: Incorporate volume profile analysis alongside TSV for a comprehensive understanding of market dynamics. By understanding where accumulation or distribution occurs at specific price levels along with volume spikes indicated by the TSV, you can spot potential support and resistance levels.
8. Trade Management: Set a trading plan with risk management in mind. This includes arranging stop-loss orders to limit losses if the market does not move in your favor. The TSV can help dictate where to place these stops — higher volume areas may signify potential bounce points or reversal zones.
9. Market Context Awareness: Always consider broader market conditions. Economic news releases or geopolitical events can significantly impact volume and market sentiment. High-impact news might lead to erratic volume patterns where the TSV can give false signals.
10. Backtesting: Before employing the TSV in live trading, backtest your strategies using historical data. This will help you gauge the effectiveness of your approach, understand the potential pitfalls, and refine your use of the indicator over time.
In summary, the Time Segmented Volume Indicator can be an invaluable asset in your trading toolkit when used properly. By focusing on confirming trends, identifying divergences, and integrating it within a broader strategy (including risk management and market context) you can enhance your trading accuracy and effectiveness. Like all indicators, TSV should not be used in isolation; a multi-faceted approach that considers risk, market conditions, and other technical signals is essential for long-term success in trading.
 If this indicator is broken,
If this indicator is broken,  Great Forex Indicators and Trading Systems for MT4 or MT5
Great Forex Indicators and Trading Systems for MT4 or MT5