Submit your review | |
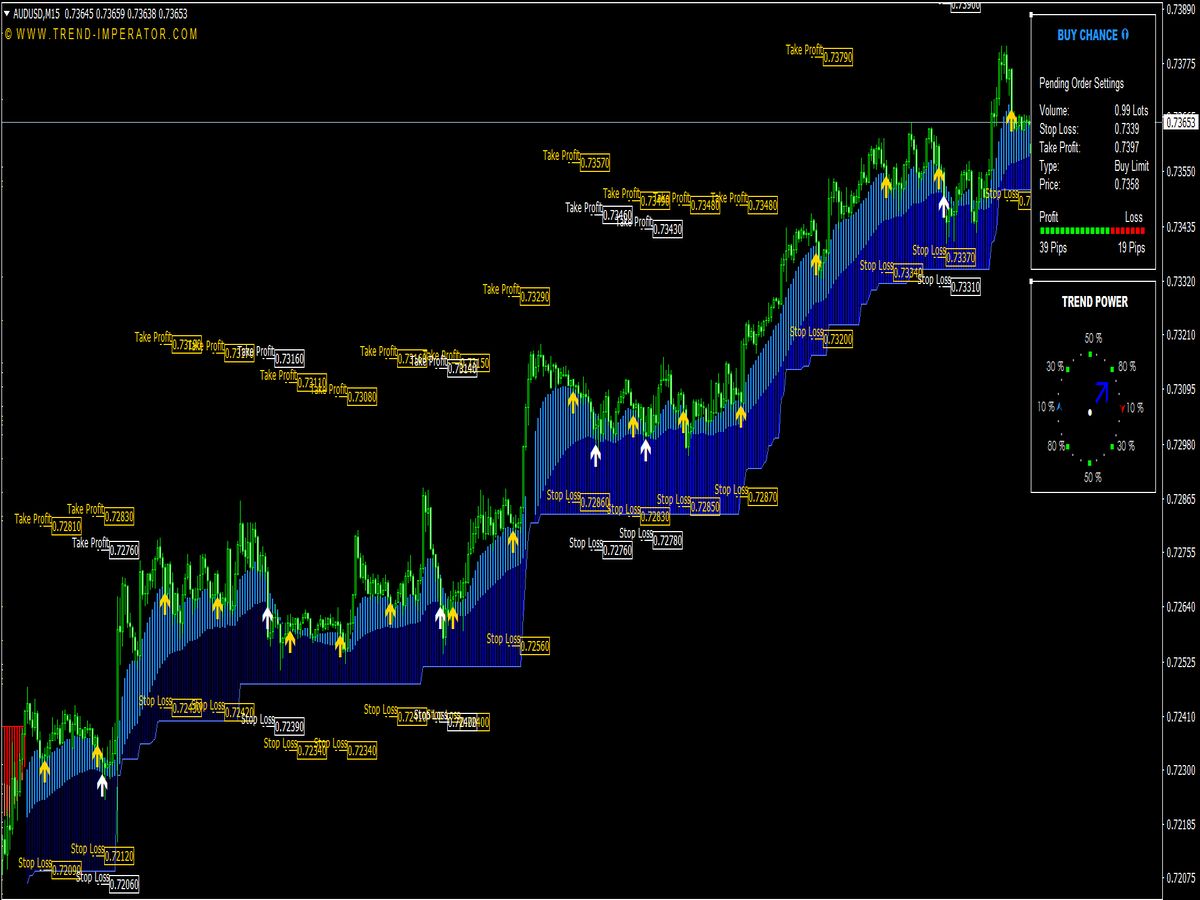
The Fair Value Gap (FVG) Indicator is a popular tool among traders, particularly in forex and futures markets, that helps identify potential reversal points by highlighting price inefficiencies. The FVG is defined as a price range where there has been little trading activity, usually following a significant price movement, suggesting that the market may return to fill this gap.
Trading Rules Using Fair Value Gap Indicator
1. Identification of Fair Value Gaps: The first step is to identify gaps in the price chart. A gap occurs when the price moves sharply up or down and leaves behind a void on the chart, which is typically marked by missing trading volume. Using the FVG Indicator, traders can quickly spot these regions.
2. Confirmation of the Trend: Before taking any trades based on the FVG, confirm the overall market trend using other technical indicators or price action. For instance, if the market is in a bullish trend, look for gaps that appear below the current price level for potential buy opportunities.
3. Entry Point: Once a Fair Value Gap is identified and the trend is confirmed, consider entering a trade when the price returns to fill the gap. For instance, if a bullish gap is found, wait for the price to retrace into this area and show signs of reversal, such as candlestick patterns (e.g., pin bars) or other technical signals (e.g., RSI divergence).
4. Stop-Loss Placement: Manage risk by placing a stop-loss order slightly below the bottom of the identified gap for long positions, or above the top of the gap for short positions. This ensures protection against unexpected price movements that can lead to losses.
5. Take Profit Targets: Set profit targets based on previous resistance levels or a favorable risk-reward ratio. Traders often aim for a target that is at least twice their stop-loss distance, creating a risk-reward ratio of 1:2 or better.
6. Time Frame Consideration: The effectiveness of the FVG Indicator can vary between different time frames. Day traders may focus on shorter periods (5-minute, 15-minute), while swing traders may look at daily or weekly charts. Choose a time frame that aligns with your trading style.
7. Volume Analysis: Consider volume analysis in conjunction with the FVG. If a gap is filled with high trading volume, it may signify stronger support or resistance at that level, leading to a more reliable trade signal.
8. Combining with Other Indicators: Enhance the FVG Indicator's effectiveness by using it alongside other technical analysis tools, such as moving averages, Fibonacci retracement levels, and momentum indicators like MACD or Stochastic. This multi-faceted approach can provide more robust entry and exit points.
9. Avoiding False Signals: Be wary of false signals, particularly in volatile markets. Ensure that the price action shows clear signs of reversals after filling the gap, and consider market sentiment or news that may influence price behavior around these levels.
10. Adaptation and Continuous Learning: Markets evolve, so it is essential to adapt your strategy as needed. Continuously backtest and analyze your FVG-based trades to understand where adjustments may be needed. Engage with trading communities or participate in forums to share insights and refine your approach.
In conclusion, the Fair Value Gap Indicator serves as a valuable tool for traders looking to capitalize on price inefficiencies. By combining gap identification with trend confirmation, disciplined entry and exit strategies, and a solid risk management plan, traders can enhance their trading effectiveness. Always remember that no indicator is foolproof, and it is vital to remain disciplined and adaptable to changing market conditions.